Archives
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-04
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-11
- 2018-10
- 2018-07
-
Dissecting DNA Fragmentation: Advanced Applications of th...
2025-09-25
Explore the advanced mechanistic and translational applications of the One-step TUNEL Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Kit in apoptosis and cell death pathway research. This article uniquely integrates emerging insights from pyroptosis studies and provides expert guidance for maximizing the kit’s power in both routine and cutting-edge experimental models.
-
Bufuralol Hydrochloride: Unraveling β-Adrenergic Blockade...
2025-09-24
Explore how Bufuralol hydrochloride, a non-selective β-adrenergic receptor antagonist, is redefining cardiovascular pharmacology research through integration with advanced human organoid and iPSC models. This article uniquely examines its mechanistic and pharmacokinetic roles in translational β-adrenergic modulation studies.
-
Optimizing mRNA Assays: EZ Cap™ Firefly Luciferase mRNA (...
2025-09-23
Explore how EZ Cap™ Firefly Luciferase mRNA (5-moUTP) advances in vitro transcribed capped mRNA applications for precise mRNA delivery and translation efficiency assays. This article provides practical insights into minimizing innate immune activation and maximizing poly(A) tail mRNA stability in mammalian systems.
-
br Autophagy inducers Macroautophagy is
2025-04-22
Autophagy inducers Macroautophagy is often seen as a cellular process capable of increasing the fitness of Sulfo-NHS-Biotin and overcome resistance to several forms of stress [9], [10]. As discussed above, it has been proposed by several authors that an effective strategy for enhancing sensitivi
-
HotStart™ 2X Green qPCR Master Mix Introduction The first us
2025-04-22
Introduction The first use of the term “autophagy” by a French physiologist, M. Anselmier, in a short article describing the effects of fasting in mice published in 1859, took place almost a century before Christian De Duve described it from a mechanistic point of view in a symposium on lysosomes i
-
br Introduction Human esophageal carcinoma is one of
2025-04-22
Introduction Human esophageal carcinoma is one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers, ranked as the eighth leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Esophagus squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the most common histological type of esophageal carcinomas, especially with a higher inci
-
Previous studies have demonstrated ATR inhibition
2025-04-18
Previous studies have demonstrated ATR inhibition is effective for treating cancers combining with chemotherapies in lung adenocarcinoma, gastric cancer, HER2 positive breast cancer and chronic lymphocytic leukemia EZ Cap™ Cy5 Firefly Luciferase mRNA (5-moUTP) to enhance chemotherapy sensitivity [[
-
Functional enhancers are often composed of
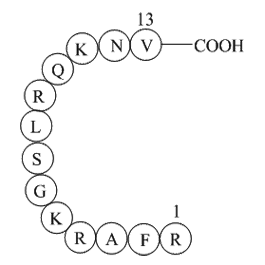
2025-04-17
Functional enhancers are often composed of binding motifs of multiple key transcription factors to confer spatial and temporal regulation of genes in a certain context. In the uterus, the difference between the number of genes that have associated PGR occupancy and that of progesterone responsive ge
-
br Conclusions and future direction ER
2025-04-17
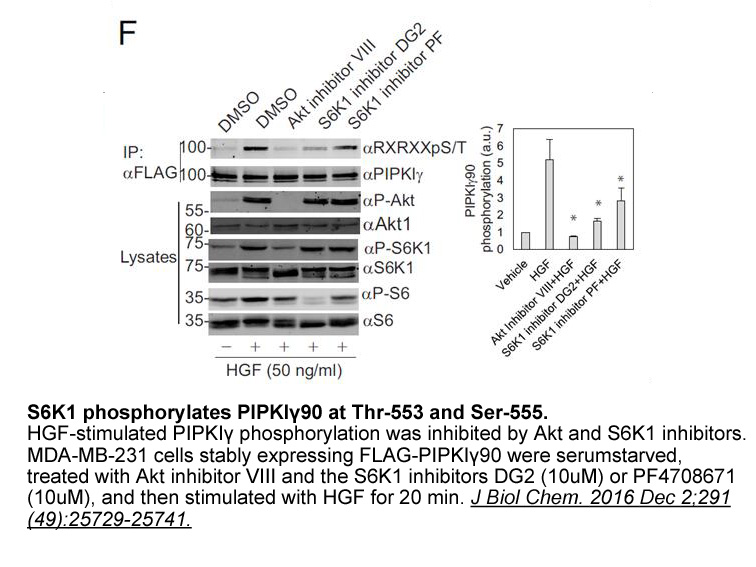
Conclusions and future direction ER(−)/PgR(+) breast cancers have a distinct clinical course, response to treatment, and molecular features when compared to other breast cancer types, however some of them are actually technical artifacts or consequences of too high definitions of positivity. Acco
-
br Author contributions br Conflicts of interest The
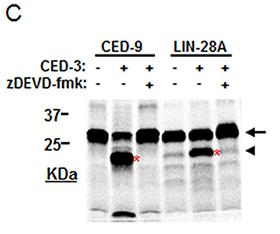
2025-04-16
Author contributions Conflicts of interest The authors declare no competing financial interests. Acknowledgement This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Sonderforschungsbereich/Transregio 166–Project C1 and grant CA 1014/1-1 to D.C.) and the IZKF Würzbur
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction resulting from mtDNA abnormalities
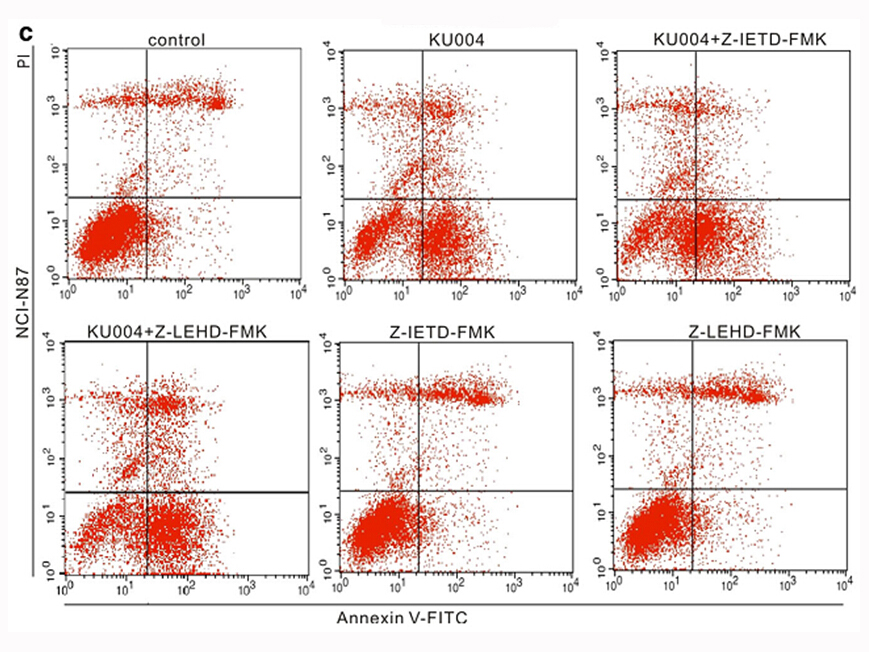
2025-04-12
Mitochondrial dysfunction resulting from mtDNA abnormalities may trigger retrograde signaling pathways from the mitochondrion to the nucleus, which regulate the expression of genes involved in diverse cellular processes, including metabolism, stress responses, tumor progression, nutrient sensing, li
-
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) br Physiology of the apelin path
2025-04-11
Physiology of the apelin pathway Role of apelin in heart disease Both apelin and apelin receptor null mice manifested moderate reduction in cardiac contractile function under basal conditions and their exercise capacity was markedly reduced (Table 1) [56]. Apelin has direct effects on the prop
-
Although apelin g kg shows negative early and
2025-04-10
Although apelin 60μg/kg shows negative (early) and positive (late) inotropic effects, since ERK1/2 phosphorylation starts at the min 5 of administration [6], ERK1/2 phosphorylation mediate positive inotropic effects of apelin 60μg/kg. After the simultaneous inhibition of KOR and APJ the phosphoryla
-
It has been proven that genetic polymorphisms can play an
2025-04-10
It has been proven that genetic polymorphisms can play an important role in development of hypertension and CVDs. In a Turkish population-based study, it was found that the APLNR gene (rs948847-A445C) polymorphism was not associated with coronary artery disease (CAD), but it was shown to be related
-
br Materials and methods br Acknowledgement This work
2025-04-10
Materials and methods Acknowledgement This work was supported by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant no. 6151001), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 31572516). Introduction Staphylococcus aureus is an important microorganism responsible for both clin
16447 records 11/1097 page Previous Next First page 上5页 1112131415 下5页 Last page